Cannabidiol, otherwise known as CBD, has grown in popularity among many people in America today and across the world. Cannabidiol is an extract of hemp plants that finds application in many pharmaceutical products. Legalizing marijuana for medicinal and relaxation purposes in the US has also helped validate its relevance and potency.
As a result, scientists have conducted lots of studies to reveal the many different ways that we can use CBD. Much more research is currently ongoing, for instance, in discovering how CBD can be used to cure certain types of cancer. In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of Epidiolex (purified CBD oil) for treating epilepsy. This article will throw more light on what CBD is, its benefits, and how it works in the body.
Understanding What CBD is?
So, what is CBD? Why is it so important?
There are over one hundred cannabinoids found in cannabis. The most common of them is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabinol (CBN), and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is the substance responsible for getting people ‘high’ when they take marijuana. CBD, on the other hand, is not a psychoactive substance. Hence it will not make you high. Instead, CBD exhibits other beneficial properties, such as reducing inflammation and pain, treating epilepsy and seizures, and treating migraine and allergies. There are many different ways in which CBD is beneficial to us, which we’ll discuss later in this piece.
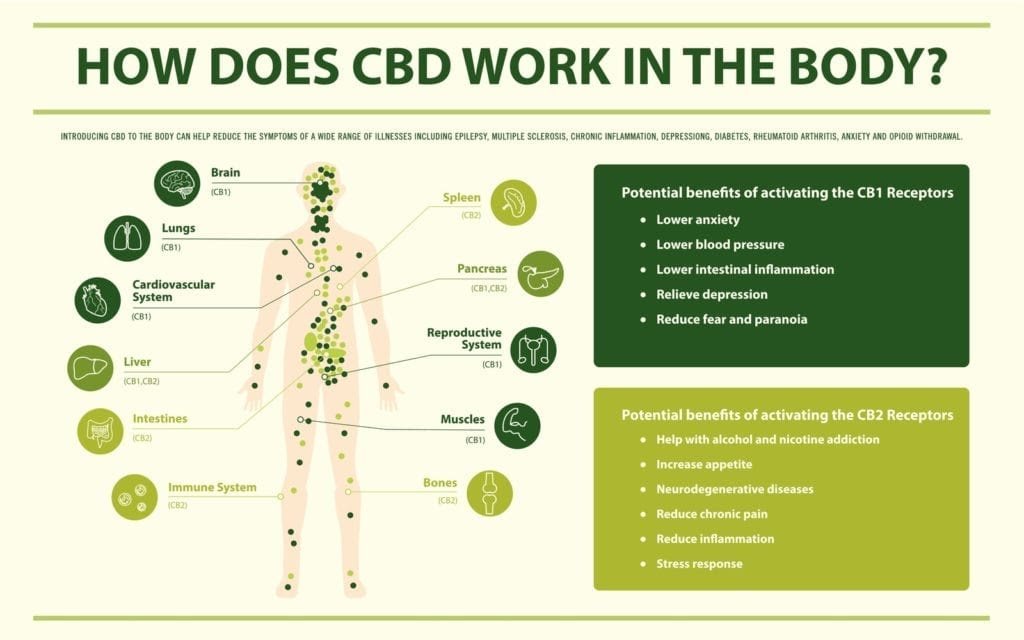
How CBD Works in the Body
Like all cannabinoids, CBD produces effects in the body by interacting with cannabinoid receptors. These receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system (more details on this in the next section).
The body produces two receptors that interact with CBD, and these are the CB1 and CB2 receptors. While THC will attach to the CB1 receptor, CBD stimulates the receptors, making the body produce endocannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are similar to cannabinoids but are produced in the body. The endocannabinoid system is composed mainly of these endogenous cannabinoids.
- CB1 receptors are present in the brain or central nervous system and every other part of the body. Their primary function is to coordinate movement, the sensation of pain, memories, emotion, mood, appetite, sleep, and other functions.
- CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are more commonly found in the peripheral nervous system. They’re involved in reducing inflammation and pain in the body.
CBD and the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system — discovered in the ’90s — is a complex biological system in the human body. It primarily consists of enzymes, endocannabinoids, and receptors that regulate many internal processes, such as appetite, sleep, mood, memory, etc. However, researchers believe that much more is yet to be known about the endocannabinoid system.
Although the various components of the endocannabinoid system function to keep the body running smoothly; the presence of CBD causes the endocannabinoids to bind to the receptors. Endocannabinoids can bind to either of the two types of receptors discussed above. The resultant effects depend on the location of the receptor that the endocannabinoid binds to.
According to research, when CBD enters the body, it is broken down by the endocannabinoid system’s enzymes. This action activates the endocannabinoids to bind to receptors. It is believed that CBD does not bind directly to the receptors but influences the binding of the endocannabinoids to receptors. In essence, it is the activation and binding of these receptors to endocannabinoids that actually produces the many health benefits people have come to associate with CBD.
Why is CBD so effective?
Remember that CBD is a non-psychoactive extract from marijuana. It is the non-psychoactive properties of CBD that confer on it the therapeutic properties for which it is known. CBD is used today in treating many medical conditions, and research provides evidence to support the effectiveness of CBD as a therapeutic substance.
For people who prefer not to vape or smoke cannabis, harvesting the medicinal value of cannabis is probably the other best way to put it to use. Some studies associate CBD with bettering heart conditions and strokes. Other studies show that it is effective in reducing seizures and managing epilepsy and treating PTSD symptoms. However, one of the most important uses of CBD today is in relieving pain and fighting inflammation.
The Benefits of CBD
Here are some common benefits of CBD in the body.
For relieving pain and inflammation
Several studies reveal that CBD has anti-inflammatory properties and can be used as a natural source for treating chronic pain.
For treating epilepsy
The FDA in 2018 finally approved the use of Epidiolex, a purified form of CBD for treating two types of epilepsy (Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome) in people aged 3 and above.
These types of epilepsy are characterized by seizures that are quite difficult to control with other kinds of medication. So far, scientists have shown that CBD can target the endocannabinoid system in a way that most synthetic drugs can’t.
For fighting cancer
Studies have also shown that CBD is effective in suppressing the growth of cancer cells. Some researchers have even suggested including CBD in chemotherapy for certain types of cancer. However, there’s a need for more research to understand how CBD combats cancer in the body and how it can be better used.
For treating Anxiety disorders
While medical experts advise that people with chronic anxiety avoid cannabis, they recommend CBD as a substance that can help reduce anxiety. THC can trigger anxiety, whereas CBD suppresses such feelings in people with conditions such as PTSD, social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and general anxiety disorder (GAD).
Acne
CBD is becoming increasingly popular in cream and skin ointments. When applied topically, CBD oil serves as an effective remedy for several skin conditions, including acne and rashes.
Other medicinal applications of CBD are in
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Allergies
- Alzheimer’s disease; and
- Migraine
Legality of CBD
While the FDA has approved CBD for medicinal purposes, there remains some uncertainty regarding specifics like dosage and side effects. However, most US states have approved the general use of marijuana for both medical and recreational use.
Under federal laws, hemp-derived CBD products with less than 0.3% THC are legal but illegal under some state laws. On the other hand, cannabis-derived CBD products are illegal under federal laws but legal under some state laws. For this reason, it is advisable to check local laws on the use of CBD, especially when you travel.
Bottom Line
For now, only one CBD product is FDA-approved, whereas CBD has properties that make it ideal for treating several other medical conditions. It is best to seek the advice of a healthcare professional before purchasing CBD products for personal use.
CBD is an effective and efficient means for consuming cannabis, but follow prescriptions provided by doctors or qualified professionals.
Source: